Embracing Millets as the Staple Diet in India: A Sustainable and Nutritious Choice
The Indian subcontinent has a rich culinary heritage, with a diverse range of staple foods, each with its own unique flavor, nutritional value, and cultural significance. While rice and wheat have traditionally been the dominant grains in the Indian diet, the time has come to explore alternative staples that can address pressing issues such as sustainability, health, and food security. Millets, a group of small-seeded grasses, are emerging as a viable and holistic solution to these challenges. This article delves into the need to adopt millets as a staple diet in the Indian context, highlighting their benefits for health, the environment, and society.
Millets: A Nutritional Powerhouse
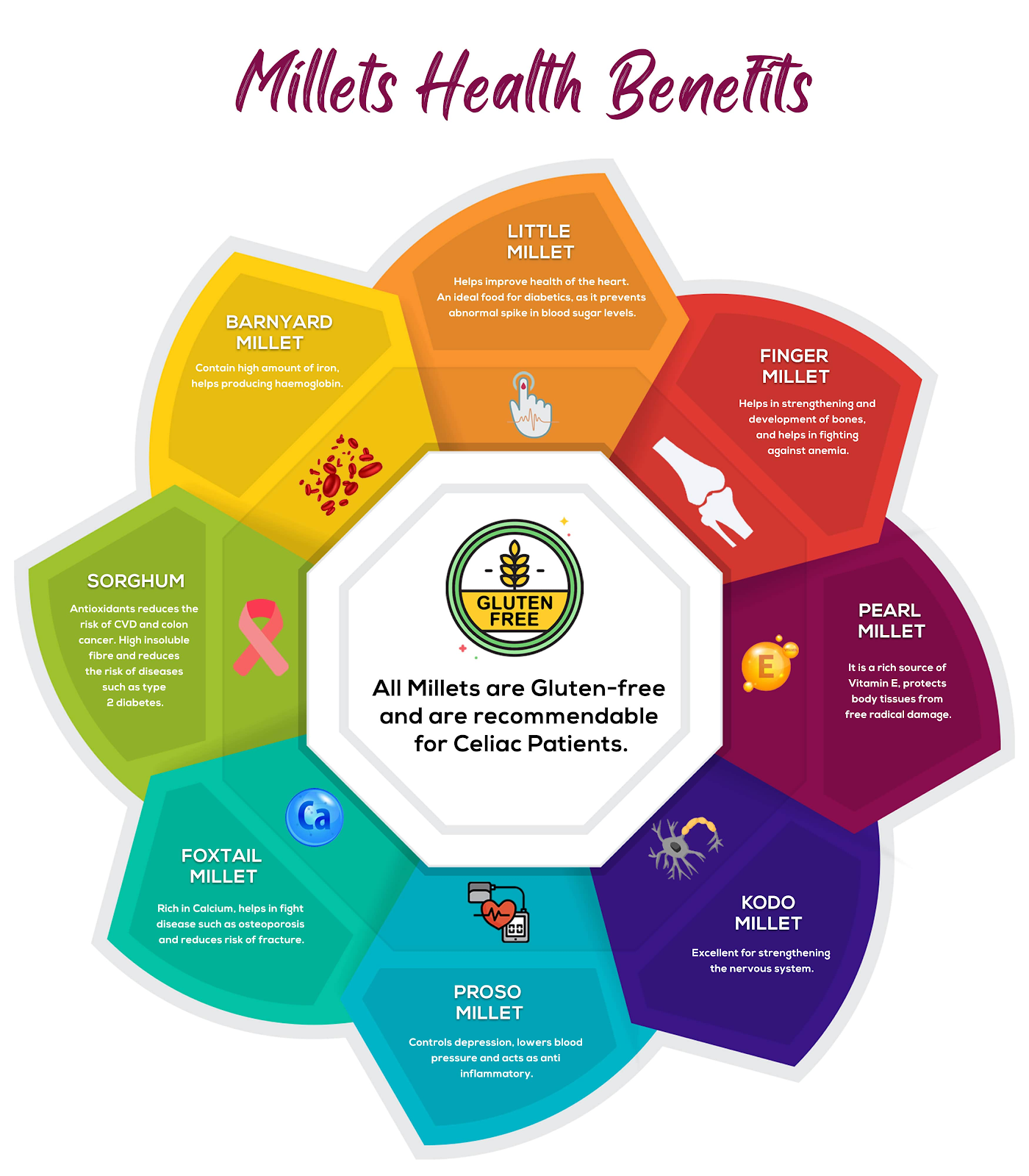
Millets are a group of small, drought-resistant grains that have been cultivated in India for thousands of years. These hardy crops include varieties such as pearl millet, finger millet, foxtail millet, and little millet. Millets are rich in essential nutrients, making them a valuable source of sustenance. They are high in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals, and they have a low glycemic index, which means they release energy slowly and help regulate blood sugar levels. Additionally, millets are gluten-free, making them an ideal choice for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
One of the standout attributes of millets is their remarkable nutrient diversity. For example, finger millet, also known as ragi, is exceptionally rich in calcium, making it a critical component for addressing India's widespread calcium deficiency. Likewise, pearl millet is a good source of iron, which can help combat anemia, a common health issue in the country. By incorporating millets into the daily diet, India can significantly improve the nutritional intake of its citizens and reduce the burden of malnutrition.
Health Benefits of Millets
The adoption of millets as a staple diet can have a profound impact on public health in India. Lifestyle diseases like diabetes, obesity, and heart conditions are on the rise, and diet plays a significant role in their prevention and management. Millets have several health benefits that can help address these concerns:
Weight Management: The high fiber content in millets can aid in weight management by promoting a feeling of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake.
Diabetes Control: Millets have a low glycemic index, which means they do not cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This makes them a suitable choice for diabetics in managing their condition.
Heart Health: Millets are heart-healthy grains. Their rich fiber and magnesium content can lower the risk of heart disease, as they help in maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Digestive Health: The dietary fiber in millets supports good digestive health and can prevent issues like constipation.
Gluten-Free: Millets are naturally gluten-free, offering a nutritious alternative for those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
3. Environmental Sustainability
In a time when environmental concerns are paramount, millets stand out as an eco-friendly choice for food production. Millet crops require significantly less water and land compared to rice and wheat. They are hardy, drought-tolerant crops that can thrive in regions with limited water resources. This attribute is especially vital in a country like India, where water scarcity is a recurring issue. By adopting millets as a staple diet, India can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of its agricultural practices.
Furthermore, millets are inherently pest-resistant and generally require fewer chemical inputs for cultivation, reducing the burden of harmful agrochemicals on the environment. Their ability to grow in diverse climatic conditions and the promotion of biodiversity in agroecosystems make millets an attractive option for sustainable agriculture.
4. Food Security
India's food security is a critical concern. With a rapidly growing population and unpredictable climatic patterns, ensuring a stable and diverse food supply is a priority. Millets can play a pivotal role in enhancing food security in the following ways:
Crop Resilience: Millets are resilient to adverse weather conditions and can withstand droughts and other climatic challenges, ensuring a more consistent food supply.
Diversification: Adding millets to the diet diversifies the sources of essential nutrients, reducing the dependency on a few staple grains and minimizing the risk of crop failures affecting food availability.
Rural Livelihoods: Promoting millet cultivation can provide employment opportunities for rural communities, thereby improving their economic well-being.
Food Sovereignty: By embracing millets, India can regain control over its food supply chain, reduce reliance on costly imports, and ensure self-sufficiency.
5. Cultural Significance
Millets have deep-rooted cultural significance in India. They have been an integral part of the country's culinary heritage for centuries. Various regions have their own traditional millet-based recipes that reflect the diversity and richness of Indian culture. Embracing millets as a staple diet can not only contribute to preserving this culinary heritage but also create a sense of pride and identity among the people.
Moreover, promoting millets can lead to a revival of age-old farming practices and traditional knowledge, fostering a stronger connection between the present and the past. This cultural significance adds an extra layer of meaning to the adoption of millets in India.
6. Challenges and the Way Forward
While the benefits of adopting millets as a staple diet are evident, there are challenges to overcome:
Awareness: Many people in India are unfamiliar with millets or may have misconceptions about their taste and preparation. Raising awareness and educating the public about the nutritional and environmental advantages of millets is essential.
Accessibility: Millets should be readily available and affordable to all segments of the population. The government and private sector need to work together to ensure easy access to millet products.
Policy Support: Government policies that incentivize millet production, processing, and marketing are crucial for their widespread adoption. These policies should include subsidies, research support, and promotion of millets in government programs.
Culinary Innovation: Chefs and food enthusiasts can play a pivotal role in creating delicious millet-based recipes to make them more appealing to consumers.
Conclusion
The adoption of millets as the staple diet in the Indian context is a transformative step that can address multiple challenges facing the nation today. By integrating millets into our daily meals, we can promote good health, protect the environment, ensure food security, celebrate our cultural heritage, and empower rural communities. To make this shift, it is crucial that individuals, communities, businesses, and policymakers collaborate to create a sustainable and nutritious food future for India. Millets offer not just a return to the past but also a pathway to a healthier, more resilient, and more vibrant future for the country and its people.








Comments
Post a Comment